Run a Symfony application using Docker and docker-compose
Why boot a full virtual machine when you can only run Docker containers of what you need to develop your Symfony applications ? This is one question asked by Jeremy Derusse at his Docker dans le développement l'intégration continue talk during Symfony Live Paris 2015. Those slides are really interesting, I invite you to take a look. They demonstrate the power of Docker and docker-compose but are waiting for practice in order to well understand. So I enjoyed a rainy week-end for further study!
Which containers do we need for a simple Symfony application?
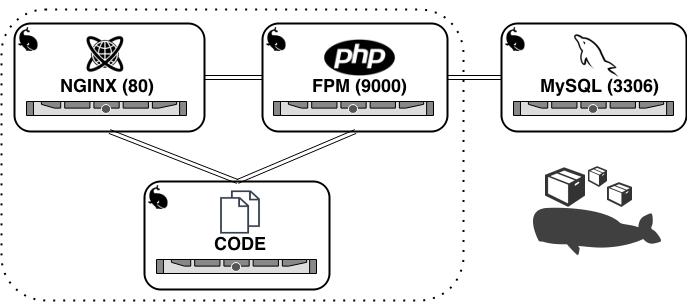
Nginx: A web server,PHP-FPM: A PHP-FPM instance which will be used by Nginx,MySQL: A database, which will be used by PHP-FPM,Symfony application: Our application code, which will be read (and also write) by Nginx & PHP-FPM.
If we now link containers together, here is what the docker-compose.yml file will look like:
application:
image: symfony/code
volumes:
- symfony:/var/www/symfony
- logs/symfony:/var/www/symfony/app/logs
tty: true
db:
image: mysql
ports:
- 3306:3306
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
MYSQL_DATABASE: symfony
MYSQL_USER: root
MYSQL_PASSWORD: root
php:
image: symfony/php-fpm
expose:
- 9000:9000
volumes_from:
- application
links:
- db
nginx:
image: symfony/nginx
ports:
- 80:80
links:
- php
volumes_from:
- application
volumes:
- logs/nginx/:/var/log/nginx
As you can see, each containers use a particular image (symfony/code, symfony/php-fpm et symfony/nginx). We have to construct and build them.
Some of those images import configuration files, all of them are available on the following Github repository I've created: https://github.com/eko/docker-symfony.
Define the symfony/code image
This is the most simple because this image will only be a container which wrap our application code in order to let it available by other containers. The Dockerfile is really simple here:
FROM debian:jessie
VOLUME /var/www/symfony
Define the symfony/php-fpm image
We will install the PHP packages (CLI & FPM) needed by our Symfony application and specify the configuration files we want to use. We also define the user identifier to 1000 for "www-data" in order that he can write data correctly. Finally, we start our PHP-FPM instance and expose the port 9000.
FROM debian:jessie
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y php5-common php5-cli php5-fpm php5-mcrypt php5-mysql php5-apcu php5-gd php5-imagick php5-curl php5-intl
ADD symfony.ini /etc/php5/fpm/conf.d/
ADD symfony.ini /etc/php5/cli/conf.d/
ADD symfony.pool.conf /etc/php5/fpm/pool.d/
RUN usermod -u 1000 www-data
CMD ["php5-fpm", "-F"]
EXPOSE 9000
Define the symfony/nginx image
Here, we install the Nginx web server and define the virtual host called for our Symfony application and location/rewrite rules. We run the web server and expose ports 80 and 443.
FROM debian:jessie
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y nginx
ADD nginx.conf /etc/nginx/
ADD symfony.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available/
RUN ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/symfony.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/symfony
RUN rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
RUN echo "upstream php-upstream { server php:9000; }" > /etc/nginx/conf.d/upstream.conf
RUN usermod -u 1000 www-data
CMD ["nginx"]
EXPOSE 80
EXPOSE 443
Let's build containers
Our containers definitions are ready to be built! We can build them by running the following commands:
$ docker build -t symfony/code code
$ docker build -t symfony/php-fpm php-fpm
$ docker build -t symfony/nginx nginx
This will result in the following created images:
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE
symfony/nginx latest 84b3420ddc51 7 hours ago 196.4 MB
symfony/php-fpm latest cc73fd15858f 7 hours ago 341.1 MB
symfony/code latest 29780cb0ca24 8 hours ago 125.1 MB
debian jessie 61e9c91c4f08 4 days ago 125.1 MB
Here we go, you can now run your containers (separately, if you want). The only thing needed now is to run the docker-compose orchestration by typing:
$ docker-compose up
You're done, you now have a full infrastructure running under Docker containers and your application is available on port 80.
Some useful commands
You can display the memory and CPU use of all your containers by typing the following command:
$ docker stats $(docker ps -q)
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE/LIMIT MEM % NET I/O
0c338e365f18 0.00% 516 KiB/1.961 GiB 0.03% 2.795 KiB/648 B
f3990e53e003 0.00% 12.74 MiB/1.961 GiB 0.63% 1.715 KiB/648 B
f7c8dd163afb 0.00% 455.9 MiB/1.961 GiB 22.70% 2.455 KiB/648 B
fdd84bfe972f 0.00% 5.109 MiB/1.961 GiB 0.25% 1.043 KiB/648 B
You can also remove all your containers and images by typing a single command:
$ docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
$ docker rmi $(docker images -q)